Resources
Highlights
Summary
In this group project, we studied the performance of a parallel ray tracing application, from CPU-based implementations to CUDA-accelerated ones.
Starting with a naïve CPU renderer, we progressively optimized the application using the right compiler flags, bounding volume hierarchies (BVH) and smarter thread scheduling strategies.
Then, we ported the C code to CUDA, a task that required the conversion of recursive functions and a completely different thread organization.
Finally, we optimized the CUDA code by introducing a tile-based thread scheduling algorithm and a better data alignment strategy, culminating in a renderer capable of achieving 65 FPS @ 1080p on a (simple) test scene, roughly 28 times faster than the best CPU implementation.
Pictures
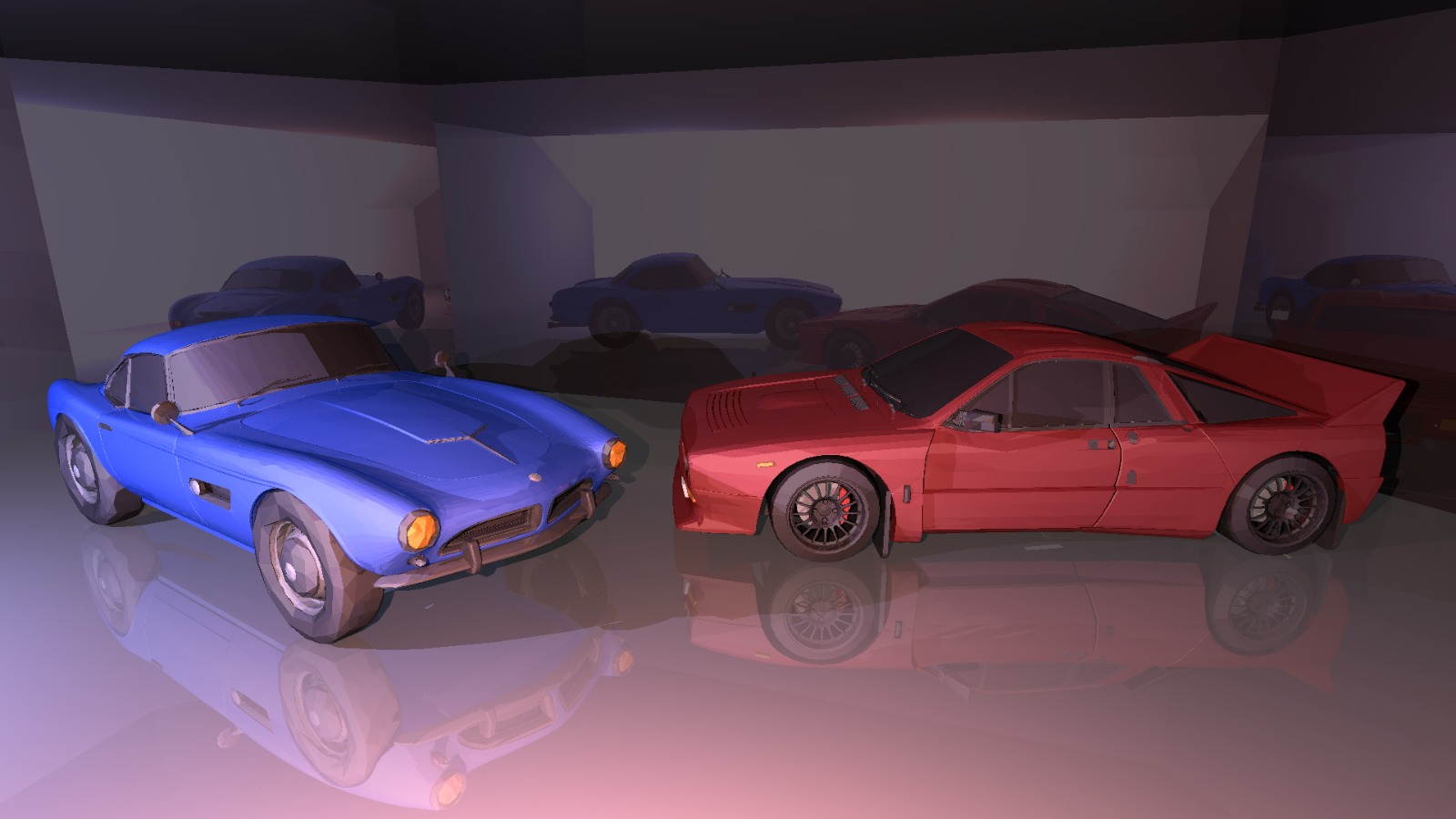

An example of rendered scene
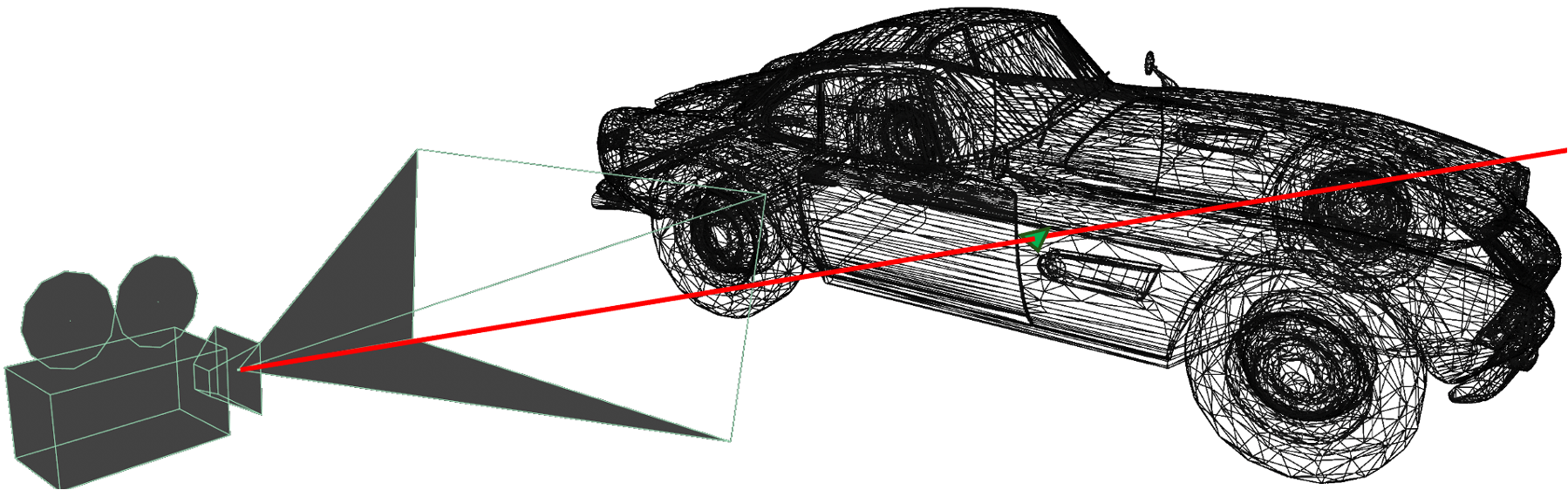
A visualization of the ray-triangle intersection process
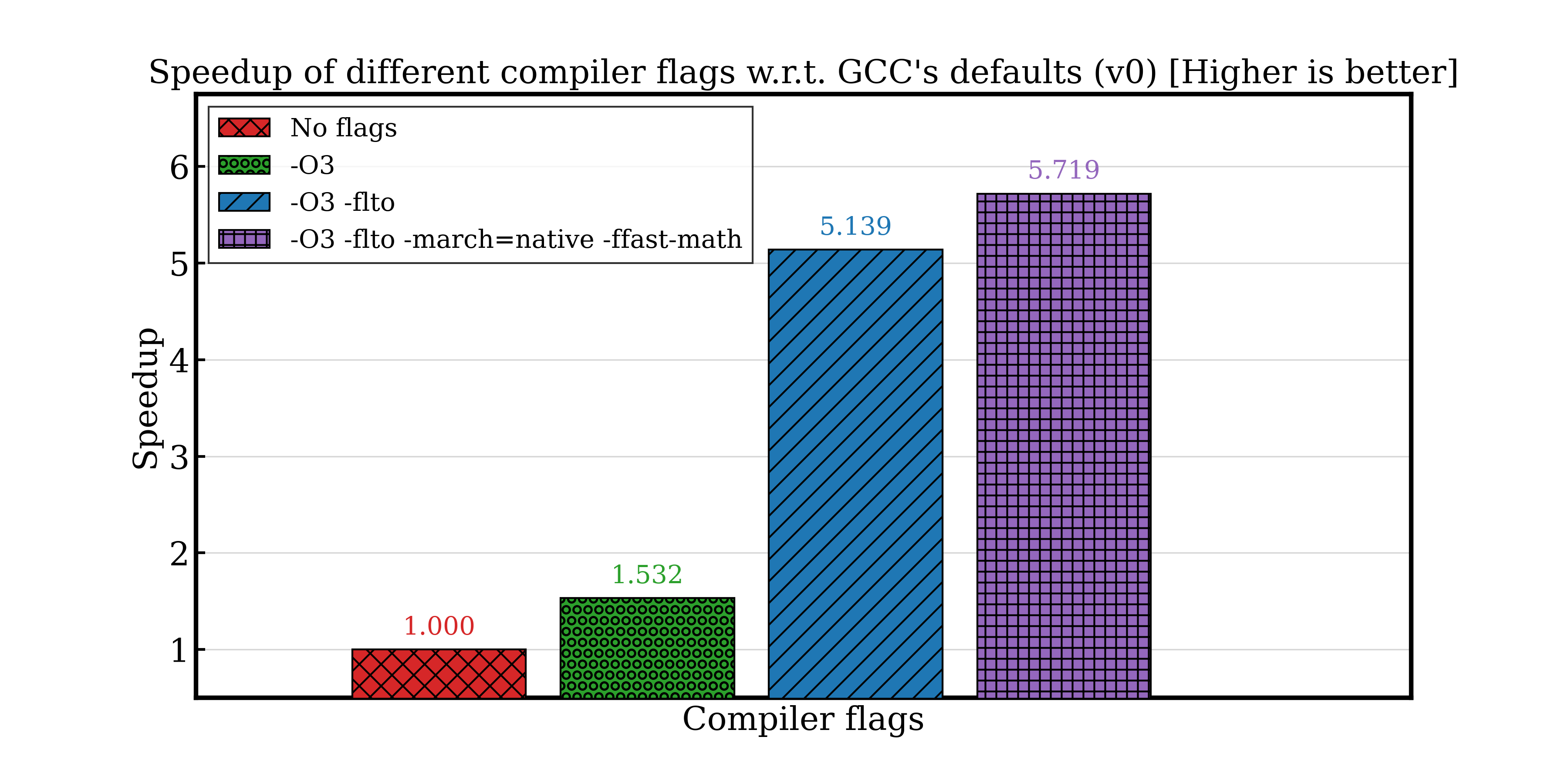
Speedup of different compiler flags with respect to GCC’s default (CPU’s naïve version)
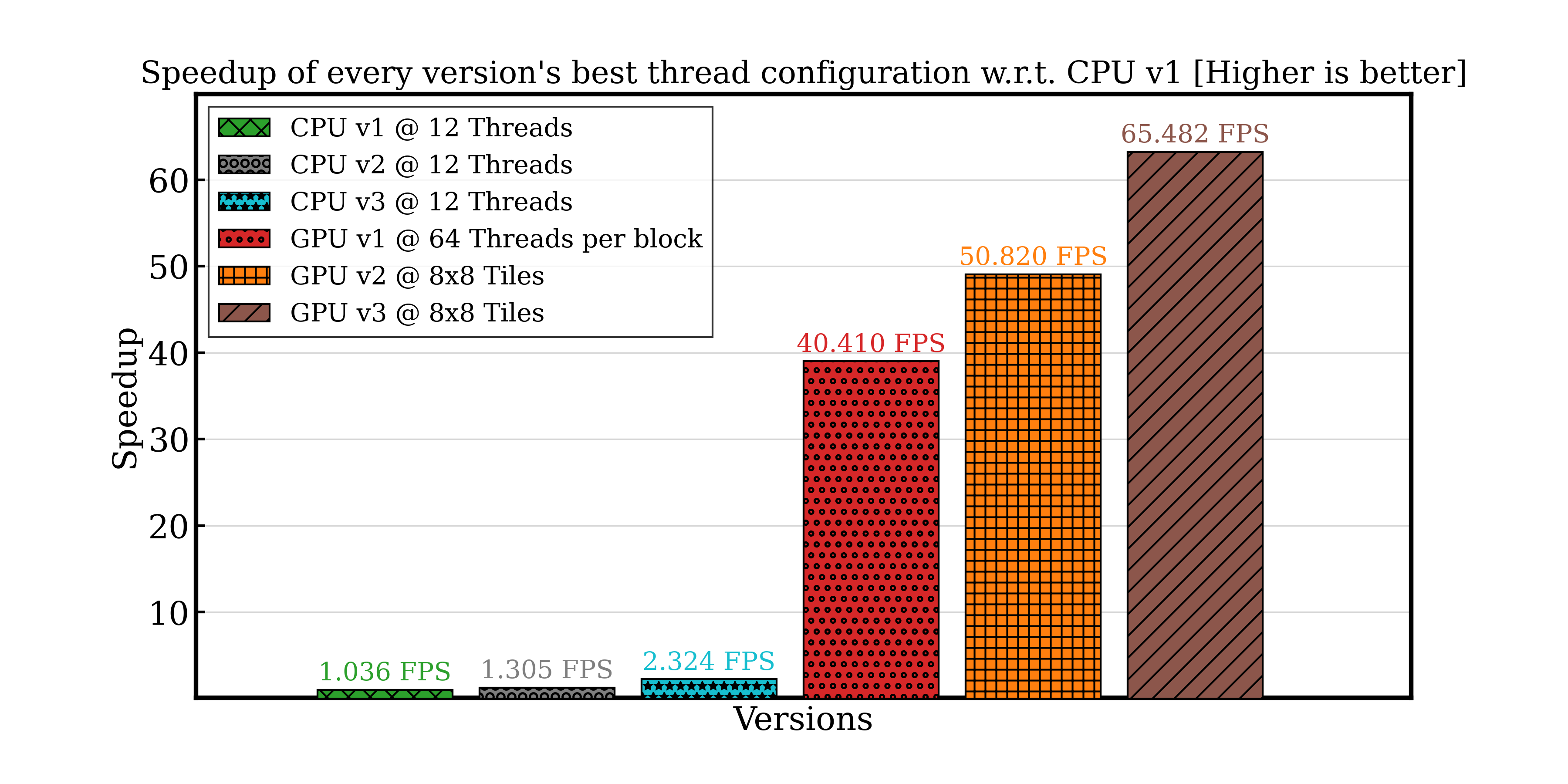
Speedup of every improved version we developed with respect to the first one