Resources
Highlights
Summary
In this group project, we explored the performance and scalability of three approaches to building an inverted index, a data structure that maps a word to the files in which it appears, widely used in database indexes and search engines.
Our work compared:
- A simple Python non-parallel script
- A Hadoop-based solution
- A Spark-based solution
We evaluated all implementations on a cluster of three nodes (courtesy of the University of Pisa) using real-world datasets from Project Gutenberg (UTF-8 books), ranging from 500 KB to 5 GB.
Thanks to the limited RAM of the nodes (7 GB), the Hadoop solution showed performance comparable to Spark when tuned properly, while Python excelled in simplicity and low memory usage for smaller datasets.
Pictures

Execution times of different combiner designs for the Hadoop solution as the size of the dataset increases
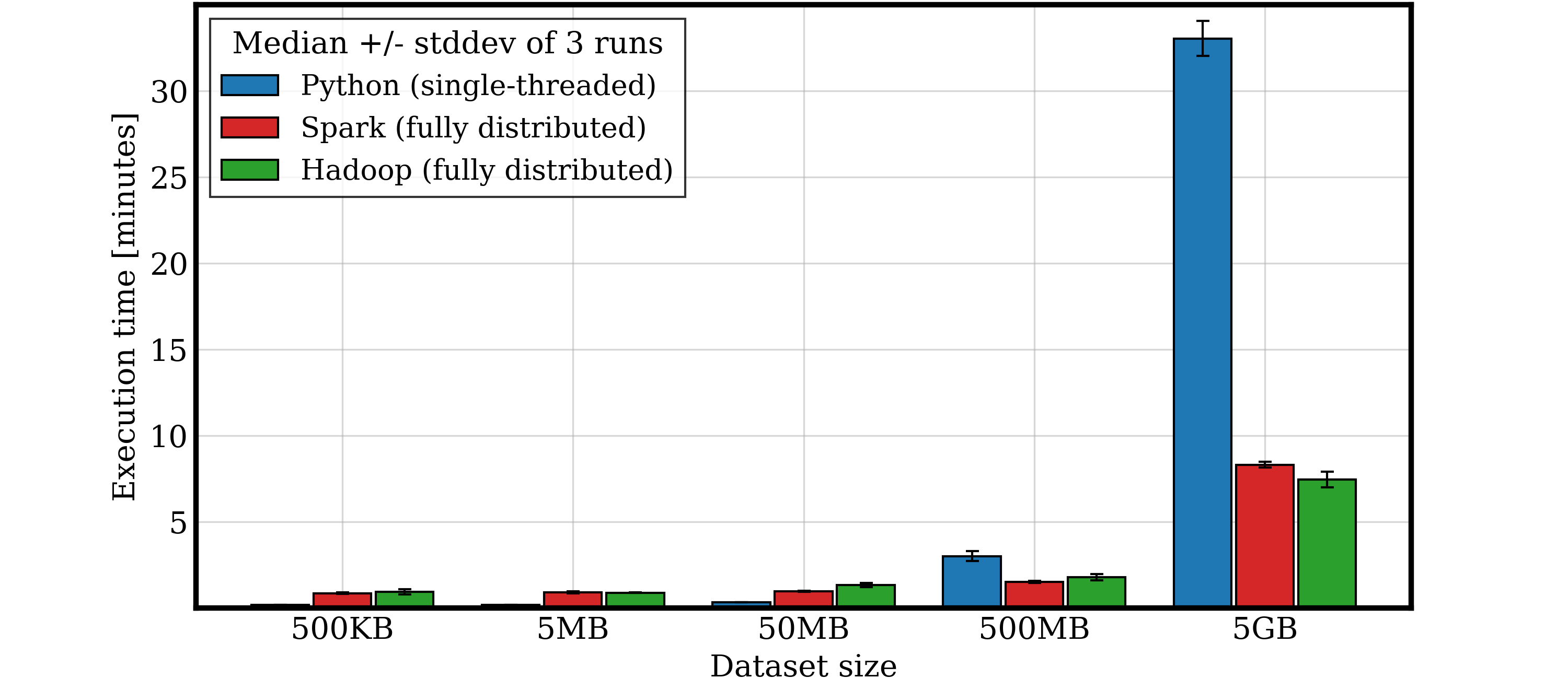
Execution times of the three different solutions as the size of the dataset increases